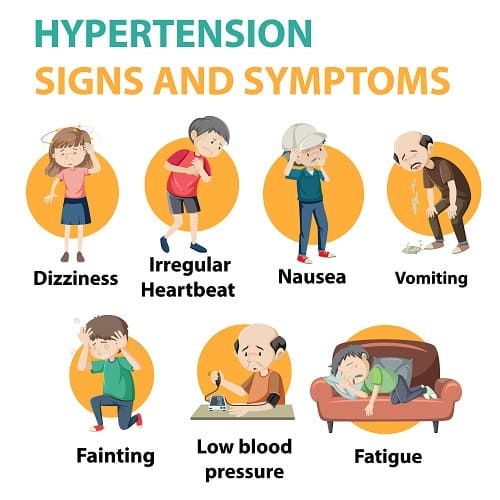
Hypertension, also known as high blood pressure, is a common health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the force of blood against the walls of the blood vessels is consistently too high. This increased pressure can have a significant impact on the body and is often referred to as the “silent killer” because it often has no symptoms.
When blood pressure is high, it places additional strain on the heart and blood vessels, leading to potential complications. The heart, which is responsible for pumping blood throughout the body, has to work harder to overcome the increased resistance. Over time, this can weaken the heart muscle and lead to heart failure.
The blood vessels themselves are also affected by high blood pressure. The constant pressure can cause damage to the inner lining of the blood vessels, making them more susceptible to plaque buildup and narrowing. This can restrict blood flow to vital organs, including the heart and brain, increasing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Understanding the impact of hypertension on the body is crucial in preventing and managing this condition. Regular monitoring of blood pressure levels, making lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly, and taking prescribed medications can help control hypertension and reduce the risk of associated complications.
The link between hypertension and heart disease
Hypertension and heart disease often go hand in hand. In fact, high blood pressure is one of the leading risk factors for the development of heart disease. The continuous strain on the heart caused by hypertension can lead to various cardiovascular conditions.
One of the most common heart conditions associated with hypertension is coronary artery disease. This occurs when the blood vessels that supply the heart muscle become narrowed due to plaque buildup. The increased pressure from hypertension can accelerate this process, leading to a higher risk of heart attacks and angina (chest pain).
Hypertension can also contribute to the development of heart failure. As the heart works harder to pump blood against increased resistance, it can become weakened and less efficient over time. This can result in symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and fluid retention.
Arrhythmias, or abnormal heart rhythms, are another potential complication of hypertension. The disrupted blood flow caused by high blood pressure can disrupt the electrical signals that control the heart’s rhythm. This can lead to conditions such as atrial fibrillation, which increases the risk of blood clots and stroke.
Managing hypertension is essential in preventing and managing heart disease. By controlling blood pressure levels through medication, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, individuals can reduce the risk of developing heart-related complications.
Exploring the risk factors for heart disease
Heart disease is a broad term that encompasses various conditions affecting the heart. While hypertension is a significant risk factor for heart disease, there are several other factors that can increase the likelihood of developing these conditions.
One of the primary risk factors for heart disease is smoking. Tobacco smoke contains harmful chemicals that can damage the blood vessels and lead to the build-up of plaque. This increases the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular complications.
Another significant risk factor is high cholesterol levels. When there is an excess of cholesterol in the blood, it can accumulate on the walls of the arteries, narrowing them and reducing blood flow to the heart. This can lead to the development of coronary artery disease and increase the risk of heart attacks.
Obesity and a sedentary lifestyle are also associated with an increased risk of heart disease. Being overweight or obese puts additional strain on the heart and increases the likelihood of developing conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol levels. Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces the risk of heart disease.
Other risk factors for heart disease include diabetes, family history of heart disease, age, and certain medical conditions such as chronic kidney disease. Understanding these risk factors and addressing them through lifestyle modifications and appropriate medical interventions can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease.
The role of hypertension in the development of stroke
Stroke, often referred to as a “brain attack,” occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted, either due to a blood clot or a ruptured blood vessel. Hypertension plays a significant role in the development of stroke by damaging the blood vessels and compromising blood flow.
High blood pressure can cause the blood vessels in the brain to become weakened and more prone to rupture. This can result in a hemorrhagic stroke, where bleeding occurs in the brain. Hemorrhagic strokes account for a smaller percentage of strokes but are often more severe and have higher mortality rates.
Another way hypertension contributes to strokes is through the formation of blood clots. When blood pressure is high, it can cause the blood to clot more easily. These clots can then travel through the blood vessels until they become lodged in a vessel in the brain, blocking blood flow and causing an ischemic stroke.
Managing hypertension is crucial in reducing the risk of stroke. By controlling blood pressure levels, individuals can minimize the damage to blood vessels and reduce the likelihood of blood clots forming. Lifestyle modifications such as maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and taking prescribed medications can help achieve optimal blood pressure control and decrease the risk of stroke.
Identifying the warning signs and symptoms of stroke
Recognizing the warning signs and symptoms of stroke is vital, as prompt medical attention can significantly improve outcomes. Common signs of stroke include sudden numbness or weakness in the face, arm, or leg, especially on one side of the body. Other symptoms may include sudden confusion, trouble speaking or understanding, severe headache, dizziness, and difficulty walking or maintaining balance.
It’s important to remember the acronym FAST when assessing for stroke symptoms:
- F: Face drooping. Is one side of the face drooping or numb?
- A: Arm weakness. Is one arm weak or numb? Ask the person to raise both arms.
- S: Speech difficulty. Is speech slurred or garbled? Ask the person to repeat a simple sentence.
- T: Time to call emergency services. If any of these symptoms are present, it’s time to call for immediate medical help.
Getting to the hospital as quickly as possible is crucial in treating stroke. Certain medications, such as clot-busting drugs, can only be administered within a specific time window to be effective. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking medical attention immediately can greatly improve the chances of a positive outcome.
Preventing hypertension, heart disease, and stroke through lifestyle changes
Prevention is key when it comes to managing hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. While there are certain risk factors that cannot be changed, such as age and family history, many lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce the risk of developing these conditions.
One of the most important lifestyle changes is adopting a healthy diet. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help control blood pressure, lower cholesterol levels, and maintain a healthy weight. Limiting the intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and foods high in saturated and trans fats is also beneficial.
Regular physical activity is another essential component of preventing hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. Engaging in moderate-intensity exercise for at least 150 minutes per week, or vigorous-intensity exercise for 75 minutes per week, can help control blood pressure, improve cholesterol levels, and maintain a healthy weight. Activities such as walking, swimming, cycling, and dancing are all excellent choices.
Avoiding tobacco smoke and limiting alcohol consumption are also crucial in preventing these conditions. Smoking damages the blood vessels and increases the risk of heart disease and stroke, while excessive alcohol intake can raise blood pressure levels and lead to other health complications.
Additionally, managing stress levels and getting enough sleep are important for overall cardiovascular health. Chronic stress can contribute to hypertension, while poor sleep quality has been associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques or engaging in hobbies, and aiming for 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night can make a significant difference.
Treatment options for hypertension, heart disease, and stroke
Treating hypertension, heart disease, and stroke often involves a combination of lifestyle changes, medication, and other interventions.
For hypertension management, lifestyle modifications are usually the first line of defense. If lifestyle changes alone are not sufficient, medications such as diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or calcium channel blockers may be prescribed to help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk of complications.
Heart disease treatment depends on the specific condition and severity. Medications to control symptoms, improve heart function, and prevent blood clots may be prescribed. In some cases, procedures such as angioplasty, stenting, or bypass surgery may be necessary to restore blood flow to the heart.
In the case of stroke, immediate medical attention is crucial. Treatment options depend on the type of stroke and may include medications to dissolve blood clots, procedures to remove clots, or surgery to repair ruptured blood vessels. Rehabilitation and lifestyle modifications are also important in the recovery process.
It’s essential for individuals affected by these conditions to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop an individualized treatment plan that addresses their specific needs and risk factors.
Support and resources for individuals affected by these conditions
Living with hypertension, heart disease, or stroke can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. However, there are numerous resources and support systems available to help individuals navigate these conditions.
Support groups, whether in-person or online, provide a platform for individuals to connect with others who share similar experiences. These groups offer emotional support, information sharing, and a sense of community.
Healthcare professionals, including doctors, nurses, and dietitians, play a crucial role in providing education, guidance, and support. They can help individuals understand their condition, manage medications, and develop personalized treatment plans.
Additionally, there are many reputable websites, educational materials, and helplines that provide reliable information and resources for individuals affected by hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. These resources can help individuals stay informed, make informed decisions, and find additional support when needed.
Conclusion: The importance of early detection and management
Hypertension, heart disease, and stroke are closely related health conditions that have a significant impact on individuals worldwide. Understanding how they are interconnected is crucial in preventing and managing these potentially devastating conditions.
Early detection and management play a vital role in reducing the risk of complications and improving outcomes. Regular blood pressure monitoring, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and seeking prompt medical attention for any warning signs or symptoms are essential steps in preventing and managing hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
By addressing the risk factors, making necessary lifestyle modifications, and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can take control of their health and significantly reduce the risk of developing these conditions. With proper management, individuals can lead fulfilling lives and minimize the impact of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke on their overall well-being.
Remember, prevention is always better than cure, and taking proactive steps today can make a world of difference tomorrow.