Understanding Liver Inflammation in Adults: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
The liver is a vital organ responsible for numerous essential functions in the human body. It plays a crucial role in digestion, detoxification, metabolism, and storage of nutrients. However, various factors can lead to liver inflammation in adults, resulting in a condition known as liver inflammation or hepatitis. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and available treatments for liver inflammation in adults.
1. What is Liver Inflammation?
Liver inflammation, also known as hepatitis, refers to the inflammation of liver cells. This condition can be acute or chronic, depending on its duration and underlying causes. Acute hepatitis typically lasts for a short period and is often caused by viral infections, excessive alcohol consumption, or exposure to certain toxins. On the other hand, chronic hepatitis is a long-term condition that progresses over time and can result from ongoing liver damage due to various factors, including viral infections, alcohol abuse, autoimmune diseases, or metabolic disorders.
2. Causes of Liver Inflammation
Liver inflammation can have multiple causes, ranging from viral infections to autoimmune diseases. Here are some common factors that can lead to liver inflammation in adults:
Viral Infections
Several viruses can infect the liver and cause inflammation. The most common viral infections associated with liver inflammation include:
- Hepatitis A: Transmitted through contaminated food or water.
- Hepatitis B: Transmitted through exposure to infected blood, unprotected sexual contact, or from an infected mother to her newborn.
- Hepatitis C: Usually transmitted through contact with infected blood, primarily through sharing needles or other drug paraphernalia.
Alcohol Abuse
Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to alcoholic hepatitis, a type of liver inflammation. Prolonged alcohol abuse can cause liver cell damage and impair liver function, leading to inflammation and potentially progressing to more severe conditions, such as cirrhosis.
Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune hepatitis is a condition in which the immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells, leading to inflammation. The exact cause of autoimmune hepatitis is unknown, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Metabolic Disorders
Certain metabolic disorders can cause liver inflammation. For example, conditions like hemochromatosis, Wilson’s disease, and alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency can lead to the accumulation of substances in the liver, causing inflammation and damage.
Medications and Toxins
Certain medications, including some prescription drugs and herbal supplements, can cause liver inflammation as a side effect. Additionally, exposure to certain toxins, such as industrial chemicals or environmental pollutants, can also contribute to liver inflammation.
3. Symptoms of Liver Inflammation
Liver inflammation may not always cause noticeable symptoms, especially in the early stages. However, as the condition progresses, individuals may experience various symptoms, including:
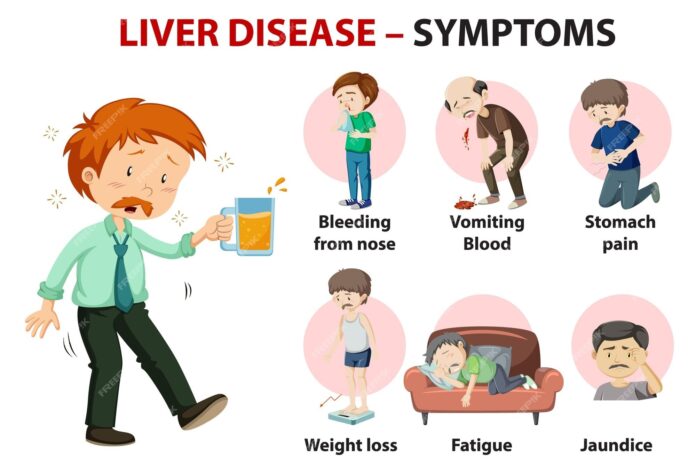
Fatigue and Weakness
Feeling excessively tired or weak is a common symptom of liver inflammation. This fatigue can be persistent and may affect daily activities and overall quality of life.
Abdominal Discomfort
Some individuals with liver inflammation may experience abdominal pain or discomfort. This pain can range from mild to severe and may be felt in the upper right abdomen, where the liver is located.
Jaundice
Jaundice is a yellowing of the skin and eyes that occurs when the liver is unable to process bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. Jaundice is a common symptom of liver inflammation and can also cause dark urine and pale-colored stools.
Appetite Changes and Nausea
Liver inflammation can affect appetite, leading to a loss of appetite or feelings of nausea. Some individuals may also experience vomiting, particularly after consuming fatty or greasy foods.
Fluid Retention and Swelling
As liver inflammation progresses, it can impair the liver’s ability to produce proteins necessary for maintaining fluid balance in the body. This can result in fluid retention, leading to swelling in the legs, ankles, and abdomen.
Skin Itching
Liver inflammation can cause itching of the skin, which may be generalized or localized to specific areas of the body. The itching can be intense and persistent, affecting sleep and daily activities.
Digestive Issues
Digestive problems, such as diarrhea or changes in bowel movements, can occur as a result of liver inflammation. Some individuals may also experience bloating or discomfort after eating.
Mental and Cognitive Changes
In advanced stages of liver inflammation, individuals may experience mental and cognitive changes due to the buildup of toxins in the brain. These changes can include confusion, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, and even personality changes.
Easy Bruising and Bleeding
Liver inflammation can affect the blood’s ability to clot properly, leading to easy bruising and bleeding. Individuals may notice frequent nosebleeds, bleeding gums, or prolonged bleeding from minor cuts or injuries.
Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss can occur in individuals with liver inflammation, particularly in advanced stages of the condition. This weight loss is often accompanied by muscle wasting and weakness.
4. Diagnosis of Liver Inflammation
If you experience symptoms of liver inflammation or have risk factors for liver disease, it is important to seek medical evaluation and diagnosis. A healthcare professional will typically conduct a thorough assessment, which may include:
Medical History and Physical Examination
Your healthcare provider will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any potential risk factors for liver inflammation. They will also perform a physical examination to assess the size and condition of your liver.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are commonly used to evaluate liver function and detect markers of inflammation. These tests can measure liver enzyme levels, such as alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), as well as assess liver function through measures such as bilirubin levels, albumin levels, and coagulation tests.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT) scan, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), may be performed to visualize the liver and assess its structure and any potential abnormalities.
Liver Biopsy
In some cases, a liver biopsy may be recommended to obtain a tissue sample from the liver for further analysis. This procedure involves inserting a needle into the liver to collect a small sample, which is then examined under a microscope to assess inflammation, scarring, or other liver abnormalities.
5. Treatment Options for Liver Inflammation
The treatment approach for liver inflammation depends on the underlying cause and the extent of liver damage. The primary goals of treatment are to manage symptoms, prevent further liver damage, and promote liver healing. Here are some common treatment options:
Lifestyle Modifications
For individuals with alcohol-related liver inflammation, the most crucial step in treatment is to stop consuming alcohol completely. Making necessary lifestyle changes, such as adopting a healthy diet, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy weight, can also support liver health.
Medications
Specific medications may be prescribed to treat the underlying cause of liver inflammation. For example, antiviral medications may be used to treat viral hepatitis, while immunosuppressive drugs may be prescribed for autoimmune hepatitis.
Symptom Management
Medications can be prescribed to alleviate specific symptoms associated with liver inflammation, such as itching, nausea, or pain. These medications aim to improve quality of life and provide relief.
Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
Regular monitoring of liver function and overall health is essential for individuals with liver inflammation. This allows healthcare professionals to assess the progression of the condition, adjust treatment plans if necessary, and detect any complications at an early stage.
Liver Transplantation
In severe cases of liver inflammation that have progressed to end-stage liver disease or liver failure, a liver transplant may be considered. This procedure involves replacing the damaged liver with a healthy liver from a donor.
It is important to note that treatment plans for liver inflammation should be individualized based on the specific circumstances of each patient. Healthcare professionals will assess the severity of the condition, the underlying cause, and any associated complications to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
6. Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
While some causes of liver inflammation, such as viral infections, may be unavoidable, there are several preventive measures and lifestyle tips that can help promote liver health and reduce the risk of liver inflammation:
- Limit alcohol consumption or abstain from alcohol altogether, especially if you have a history of alcohol-related liver inflammation.
- Practice safe sex and take precautions to prevent the transmission of viral infections, such as hepatitis B and hepatitis C.
- Avoid the sharing of needles or other drug paraphernalia to reduce the risk of contracting viral infections.
- Practice good hygiene and food safety measures to prevent infections that can lead to liver inflammation, such as hepatitis A.
- Be cautious when taking medications, and follow the recommended dosage instructions. Avoid excessive use of over-the-counter pain relievers, especially those containing acetaminophen.
- Maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise. Obesity and excessive weight gain can contribute to the development of fatty liver disease and subsequent inflammation.
- Stay up to date with vaccinations, particularly those for hepatitis A and hepatitis B, if you are at an increased risk.
- Avoid exposure to toxins and chemicals that can damage the liver. Follow safety guidelines when working with hazardous substances.
- If you have a family history of liver disease or are at an increased risk, consider regular screenings and consultations with a healthcare professional to monitor liver health.
Conclusion
Liver inflammation, or hepatitis, can have various causes and can range from acute and self-limiting to chronic and potentially life-threatening. Recognizing the symptoms of liver inflammation and seeking medical evaluation is crucial for early detection and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to promote liver health, prevent liver inflammation, and minimize the risk of complications. Remember, always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice and guidance regarding your specific health needs.